HAProxy Load balancer setup with Ansible
What Is HAProxy?
HAProxy is a free, very fast, and reliable solution offering high availability, load balancing, and proxying for TCP and HTTP-based applications. Load balancers like HAProxy allow you to split traffic over multiple servers, making it easier to handle. Instead of pointing your IP at your web server, you’d point it at an HAProxy server, which would decide where to send it from there. Since it is light weighted, you can use a single load balancer for many backend servers.
Since we are going to use the HAProxy as the load balancer for k8s control plane nodes master1 and master2.
Three steps:
1. Install HAproxy software
2. configure backend servers
3. Start the service
Step1: Installation of haproxy package with Ansible configuration management tool.
$ # execute the below snippet and run the ansible-playbook with the below command.
cat <<EOF> haproxy.yaml
- name: HAProxy install
hosts: lb
gather_facts: no
become: yes
tasks:
- name: Install software
package:
name: haproxy
state: present
EOF
$ ansible-playbook -i inventory ha-proxy.yaml --ask-become-pass
Step2: Backend Servers block configuration using jinja2 templates.
create templates folder under the current working directory and use the below template as a reference.
First snippet:
cat <<EOF> templates/haproxy.j2
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Example configuration for a possible web application. See the
# full configuration options online.
#
# https://www.haproxy.org/download/1.8/doc/configuration.txt
#
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Global settings
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
global
# to have these messages end up in /var/log/haproxy.log you will
# need to:
#
# 1) configure syslog to accept network log events. This is done
# by adding the '-r' option to the SYSLOGD_OPTIONS in
# /etc/sysconfig/syslog
#
# 2) configure local2 events to go to the /var/log/haproxy.log
# file. A line like the following can be added to
# /etc/sysconfig/syslog
#
# local2.* /var/log/haproxy.log
#
log 127.0.0.1 local2
chroot /var/lib/haproxy
pidfile /var/run/haproxy.pid
maxconn 4000
user haproxy
group haproxy
daemon
# turn on stats unix socket
stats socket /var/lib/haproxy/stats
# utilize system-wide crypto-policies
ssl-default-bind-ciphers PROFILE=SYSTEM
ssl-default-server-ciphers PROFILE=SYSTEM
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# common defaults that all the 'listen' and 'backend' sections will
# use if not designated in their block
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
defaults
mode http
log global
option httplog
option dontlognull
option http-server-close
option forwardfor except 127.0.0.0/8
option redispatch
retries 3
timeout http-request 10s
timeout queue 1m
timeout connect 10s
timeout client 1m
timeout server 1m
timeout http-keep-alive 10s
timeout check 10s
maxconn 3000
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# main frontend which proxys to the backends
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
frontend main
bind *:6443
acl url_static path_beg -i /static /images /javascript /stylesheets
acl url_static path_end -i .jpg .gif .png .css .js
use_backend static if url_static
default_backend app
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# static backend for serving up images, stylesheets and such
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
backend static
balance roundrobin
server static 127.0.0.1:4331 check
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
# round robin balancing between the various backends
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
backend app
balance roundrobin
{%for host in groups['master'] %}
server {{hostvars[host].inventory_hostname}} {{hostvars[host].ansible_host}}:6443 check
{%endfor%}
EOF
second snippet:
cat <<EOF> haproxy-config.yaml
- name: haproxy configuration
hosts: lb
become: yes
tasks:
- name: haproxy config template
template:
src: haproxy.j2
dest: /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
EOF
$ ansible-playbook -i inventory haproxy-config.yaml --ask-become-pass
Step3: Start the HAproxy service and validate the service.
$ # execute the below snippet and run the ansible-playbook with the below command.
cat <<EOF> haproxy-config.yaml
- name: start the haproxy service
gather_facts: no
hosts: lb
become: yes
tasks:
- service: name=haproxy state=started
EOF
$ ansible-playbook -i inventory haproxy-service.yaml --ask-become-pass
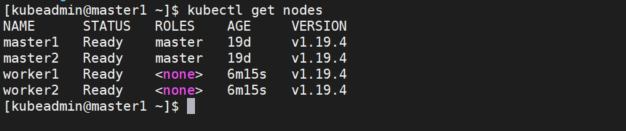
Now that our front-end service was ready, we can move forward to install the control plane and worker nodes setup to form a HA k8s cluster.


Comments
Post a Comment